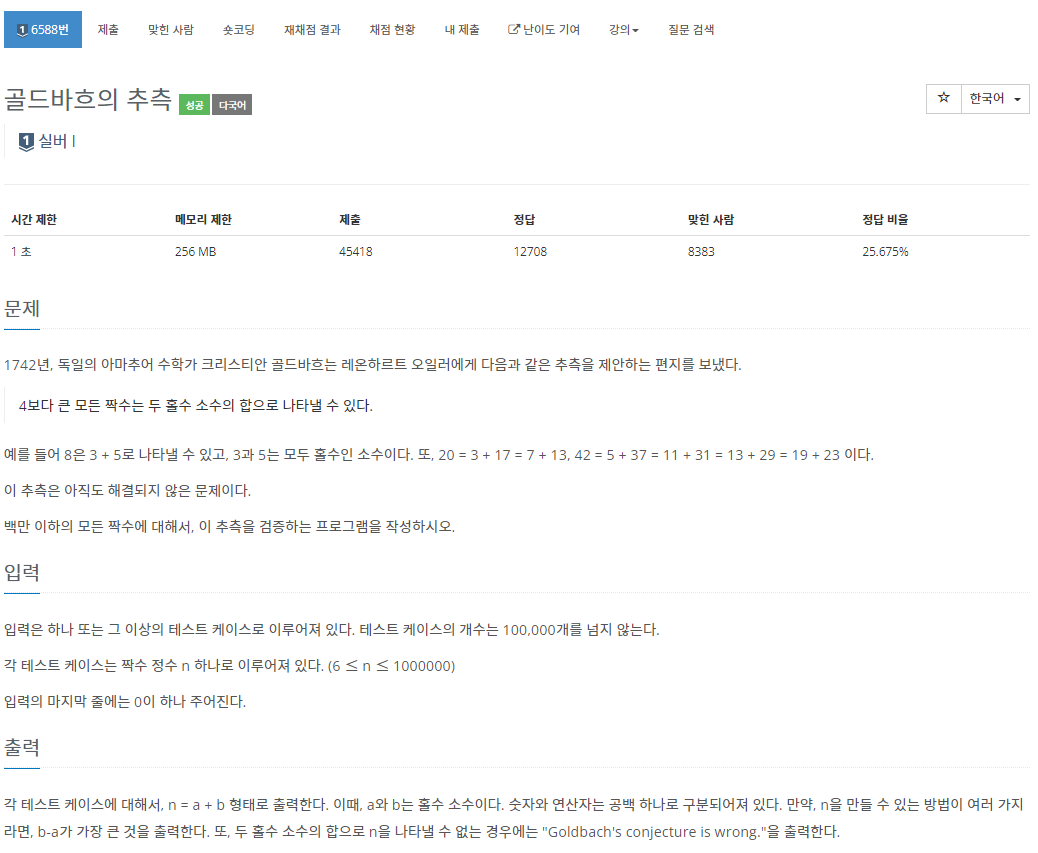
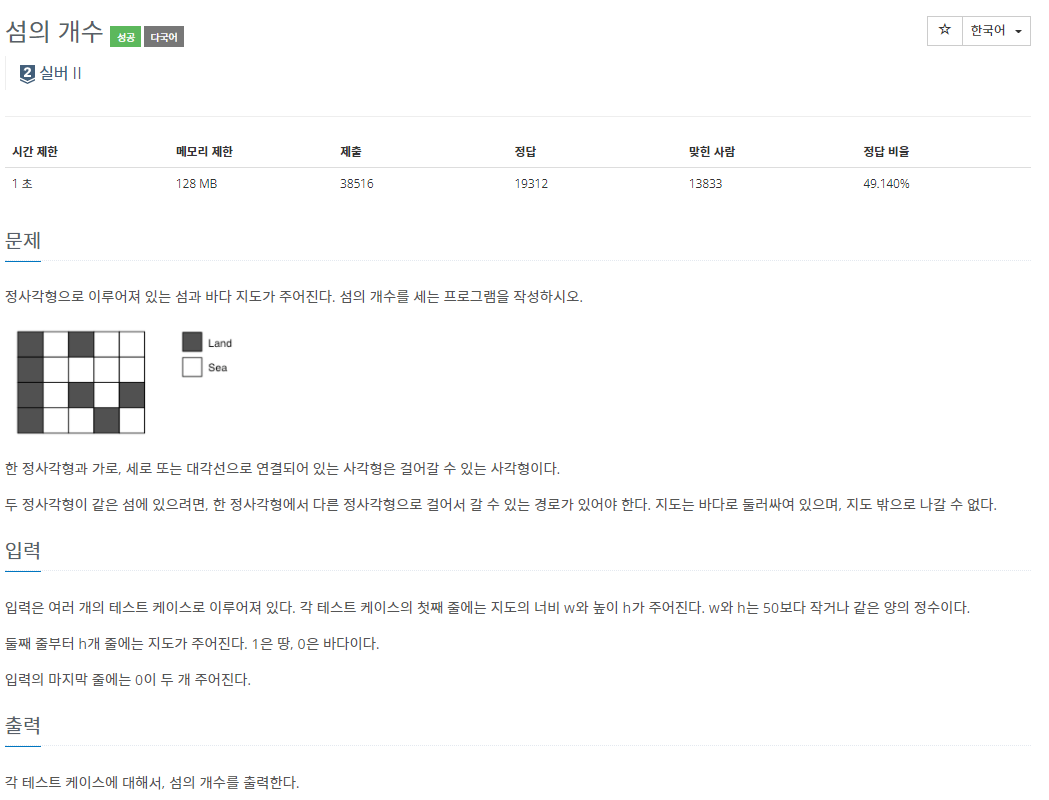
-표준 국어 대사전에서 발췌-
일반적으로 재귀함수에서 더 이상의 호출이 의미 없을 때, 중간에 재귀함수를 중단시키는 알고리즘을 의미한다.
백준 14889번, 15661번 스타트 링크 문제를 통해 백트래킹에 대해 알아보자.
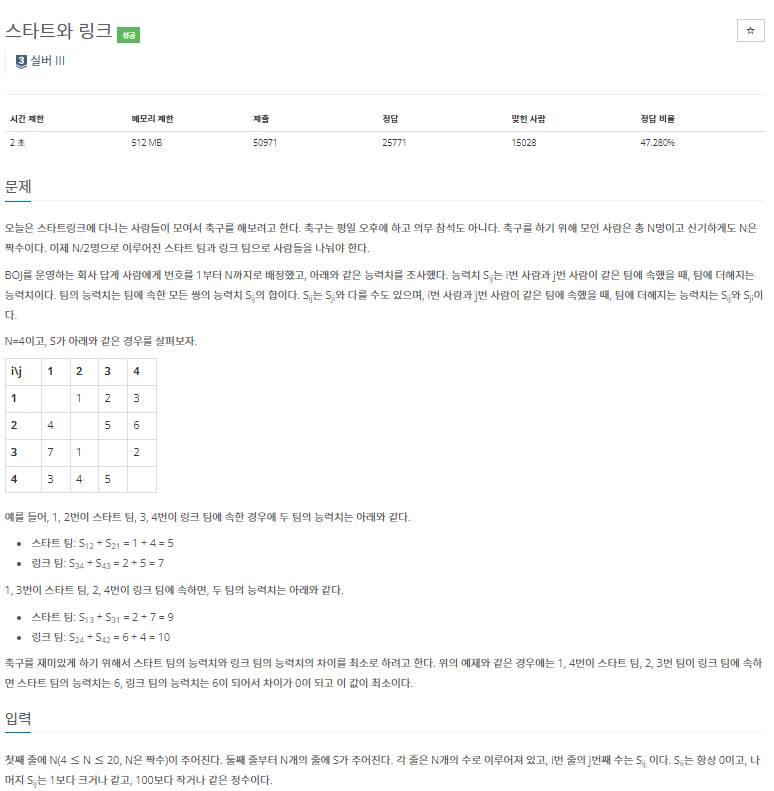
1 ~ N까지의 번호 중 2개의 팀을 각 N/2명으로 나누어야 한다.
2. 이때 S[I][J] = i번 사람과 j번 사람이 같은 팀일 때 팀에 더해지는 능력치이다.
3. 팀의 능력치 : 팀에 속한 모든 s[i][j]쌍의 합이다.
4. 문제 요구 사항 : 두 팀의 능력치를 구하고 차이의 최소를 구하라
해당 문제를 요구 사항에 맞게 코딩하면
def go(index, first, second):
if index == n:
if len(first) != n // 2:
return -1
if len(second) != n // 2:
return -1
t1 = 0
t2 = 0
for i in range(n // 2):
for j in range(n // 2):
if i == j:
continue
t1 += s[first[i]][first[j]]
t2 += s[second[i]][second[j]]
diff = abs(t1 - t2)
return diff
ans = -1
t1 = go(index + 1, first + [index], second)
if ans == -1 or (t1 != -1 and ans > t1):
ans = t1
t2 = go(index + 1, first, second + [index])
if ans == -1 or (t2 != -1 and ans > t2):
ans = t2
return ans
n = int(input())
s = [list(map(int, input().split())) for _ in range(n)]
print(go(0, [], []))이런 코드가 나오게 된다.
index : 사람을 어떤 팀에 넣을지 (스타트 팀, 링크 팀)
first : 1번 팀, second : 2번 팀
index == n 일 경우 함수 종료
first나 second의 팀 수가 n//2를 넘어가게 되면(딱 절반이어야 하는데 넘어갈 때) -1 반환
하지만 index == n 일때
first나 second가 n//2가 아님을 검사하게 되면
결국 index는 n 만큼의 재귀를 실행하게 된다.
만약 first나 second가 (n이 8일 때) 5를 넘었을 때 바로 종료한다면 더 시간을 단축할수 있을 것이다.
이때를 위해 백트래킹 방법이 사용된다.
재귀 중간에, 특정 상황(의미 없는 재귀가 반복된다고 판단)에서 재귀를 종료시키는 구문을 넣어준다.
def go(index, first, second):
if index == n:
if len(first) != n // 2:
return -1
if len(second) != n // 2:
return -1
t1 = 0
t2 = 0
for i in range(n // 2):
for j in range(n // 2):
if i == j:
continue
t1 += s[first[i]][first[j]]
t2 += s[second[i]][second[j]]
diff = abs(t1 - t2)
return diff
ans = -1
if len(first) > n // 2:
return -1
if len(second) > n // 2:
return -1
t1 = go(index + 1, first + [index], second)
if ans == -1 or (t1 != -1 and ans > t1):
ans = t1
t2 = go(index + 1, first, second + [index])
if ans == -1 or (t2 != -1 and ans > t2):
ans = t2
return ans
n = int(input())
s = [list(map(int, input().split())) for _ in range(n)]
print(go(0, [], []))
따라서 중간에
if len(first) > n // 2:
return -1
if len(second) > n // 2:
return -1
를 넘어줌으로써, 시간을 절약시킬 수 있다.
'파이썬 (Python) > 파이썬 알고리즘 (Python Algorithm)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [22-03-10] 학습일지 - 유니온 파인드(Union-Find) (0) | 2022.03.10 |
|---|---|
| [22-03-10] 학습일지 - Kruskal 알고리즘(최소비용신장트리) (0) | 2022.03.10 |
| [파이썬] 21-12-26 학습일지 다이나믹 프로그래밍 (0) | 2021.12.26 |
| [파이썬] 그래프 탐색의 A to Z, DFS와 BFS (0) | 2021.12.18 |
| [Greedy Algorithm] 탐욕적인 알고리즘, 그리디 (0) | 2021.12.03 |